Viewing in swimming pools falls under one of three types:
1. Informal viewing:
which is the general viewing for understanding the layout of the of he building allowing a degree of supervising. It can be both internally or externally.
2. Formal viewing:
which require fixed seating that is usually stepped and located on the long side of the pool - usually the competitive pool-.
3. Pool surrounds:
which is the seating along the pool for competitors in events. Depending on the situation those seating can be temporary seating but it has to take the general circulation in accounts.
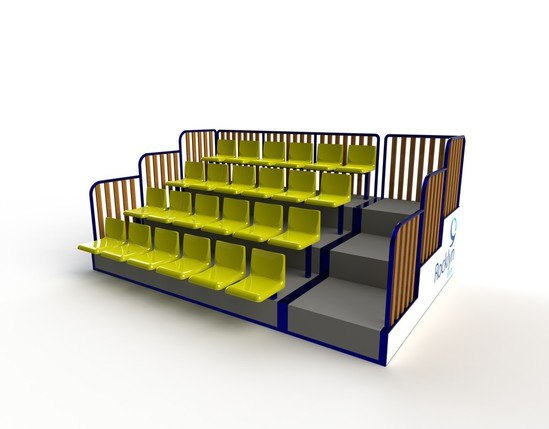
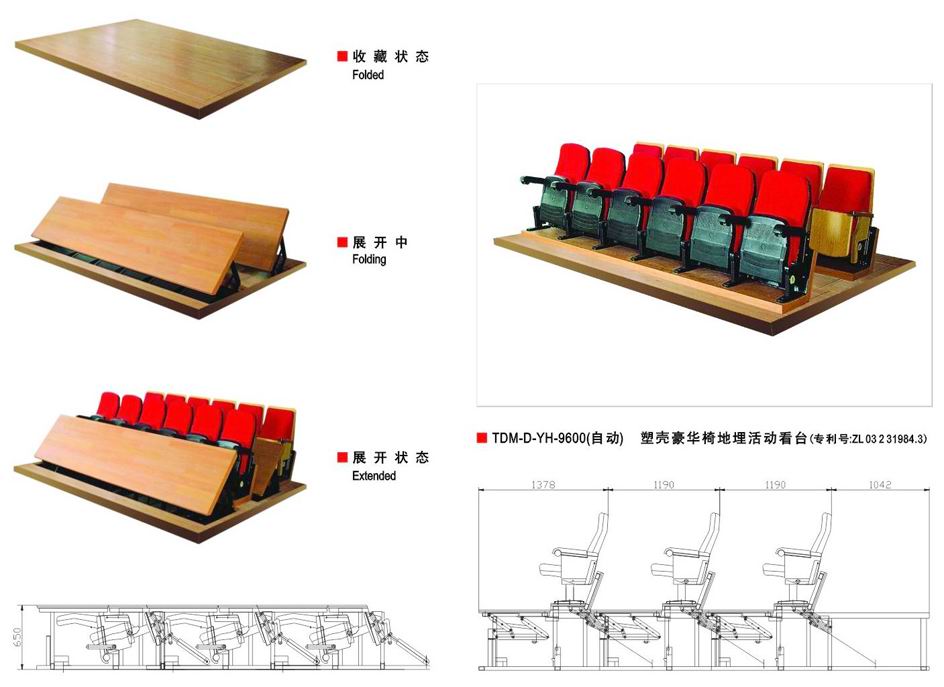
Seating capacity:
Dimension:
Spectator seating should be designed to meet the "Guide to Safety at Sports Grounds - (The Green Guide):
1- The maximum angle of seating rake should not exceed 34˚.
2- The ‘C value’ or distance of the sight line above the head of the person in the row in front and the ‘focus point. The minimum C value should be 0.090 m, but
0.120 m is preferred.
3. The space below the seating might be used as changing rooms or pool storage
depending on the layout and the height the seating.
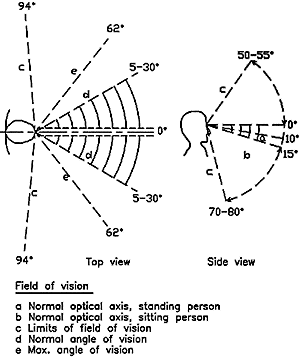
4. Sight lines should relate to a focus point at the edge of the pool, particularly in 10 lane pools where all lanes may be used (the red line in the figure above ).
5. Riser heights ( N value) and seating row depths ( T value) will generally be a function of multiples of 0.28 m minimum goings and 0.19 m maximum risers
Accessibility
Accessibility for wheelchair users needs to be considered early in the design. In smaller facilities, accessibility may only be practical at pool side and/or the uppermost level of the seating.
Seating Details:
Steps and levels:
Creativity: